What is Ankle Fracture?
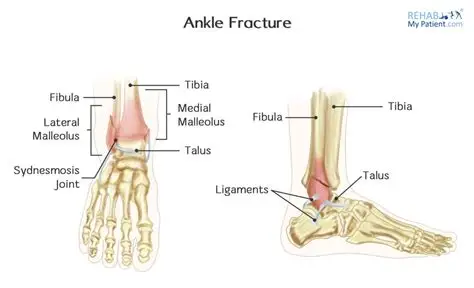
A fracture is a bone break or a crack in the bone. In an ankle, three different bones can be fractured tibia, the larger of the two bones in the lower leg. The tibia's lower end forms a hard, bony knob, called the medial malleolus, which can be felt at the inner side of the ankle, another bone is the fibula, and its lower end forms a hard, bony knob, called lateral malleolus, which can be felt at the outer side of the ankle. And the third bone is the talus, which is a wedge-shaped bone located inside the ankle, between the heel bone and the ends of the tibia and fibula. The talus supports the lower ends of the tibia and fibula and forms a solid base for the normal range of ankle movements.
With each bone, the fracture will be either:
- Non-displaced: Bones are broken but they are still in correct position and alignment.
- Displaced:
Symptoms OF Ankle Fracture
Symptoms depend on the type of injury, the most common symptoms include:
- Pain on the lower leg
- Swelling at the ankle
- Tenderness
- Bruising at the ankle joint
- Inability to move the ankle through its normal range of motion
- Inability to take weight on the injured ankle
- Snap or cracking sounds in the ankle at the time of injury
Pathology: Ankle fractures are caused by accidents, sharp blows, or bone infections, which the ankle fails to resist causing a break or fracture. They can usually involve nerves, ligaments, muscles, and tendons.
Causes of Ankle Fracture
There are many causes of ankle fracture, few of them are mentioned below:
- A sharp twist of the ankle
- Athletic activities, including ballet dancers, snowboarders, basketball players, and skydivers
- During slipping on icy pavement
- Fall from a high place
- Motorcycle accidents like direct impact to the ankle during a car crash
- High-impact ankle injuries
Diagnosis Of Ankle Fracture
Physical Examination: The examiner reviews the medical history, and previous injuries to the ankle, foot, or lower leg. The examiner checks for swelling, deformity, soreness, abrasions, and bruising along the lower part of the tibia and fibula, especially at the medial malleolus and lateral malleolus. The examiner also gently presses and feels the parts of the injured ankle to determine the points of extreme tenderness to identify the site of a fracture. The range of motion of the injured ankle with the normal joint movement of the uninjured ankle is compared. After a significant injury, the pulse, foot movements, and skin sensation are also checked to see the signs of artery or nerve damage.
CT scan: CT scan provides a clear and detailed image of the cross-section image of the ankle.
MRI: Magneto resonance imaging (MRI) is used to determine bone as well as soft tissue injury.
X-ray: X-ray is used to determine whether there is a broken bone as opposed to a soft-tissue injury like a sprain since ankle sprains and breaks have similar symptoms.
Treatment Of Ankle Fracture
Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, etc.
Note: Medication should not be taken without the doctor’s prescription.
Surgery: Surgery is recommended if there is more extensive damage to the ankle, or the fragments of the broken bone are separated far from one another. Surgery is performed to repair the fractured ankle with special screws or wires.
Physiotherapy Treatment Of Ankle Fracture
Rest: Immobilization is done with the help of a cast or a brace to hold the ends of the bones in a resting position. Ankle brace provides additional support in case of chronic stiffness or weakness in the joint.
Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves the application of ice over the ankle joint for around 30 minutes, two to three times a day.
Range of motion exercises: Simple range of motion exercises are recommended in the pain-free range to increase joint movement such as ankle dorsiflexion, ankle plantar flexion, etc.
Thermotherapy: Thermotherapy is applied to the ankle joint to increase blood circulation.
Weight Bearing: Weight-bearing exercise is initially limited to gently touching the floor with the toe, with the help of a walker, crutches, or cane, but as the ankle heals, the muscles strengthen, and more and more weight is put on the ankle.
Transcutaneous Electrical stimulation: TENS is used to reduce pain and inflammation in the ankle and also helps to improve the strength of the muscle.
Laser Therapy (LLLT): Laser therapy helps to accelerate callus formation and thus enhance the healing process.
Therapeutic Ultrasound: Ultrasound therapy helps to break the adhesions resulting in decreased pain and an increase in the range of motion.
Stretching and strengthening Exercises: Stretching exercises are done to decrease stiffness, increase flexibility, and increase range of motion. Strengthening exercises include isometrics, isotonic, and isokinetic exercises and also using therabands and weights.
Balance and proprioception exercises: Balance and proprioception exercises are recommended with a bobath ball or on a wobble board.
Patient Education
The patient is advised to play sports with care, to prevent the reoccurrence of ankle fracture. High-top shoes, ankle taping, or an ankle brace can also reduce the risk of further joint damage.